
BACKGROUND
The reason for developing this procedure was two-fold.
see this forum thread for more information on that subject K2.6 Increase Maximum Connections ip_conntrack_max hashsize
I developed this procedure on a WRT54G-TM Linksys/T-mobile router. The router is flashed with dd-wrt.v24_mega with a kernel 2.6 kernel, build 13972. This procedure should work with other 2.6 kernel builds however I have not verified this.
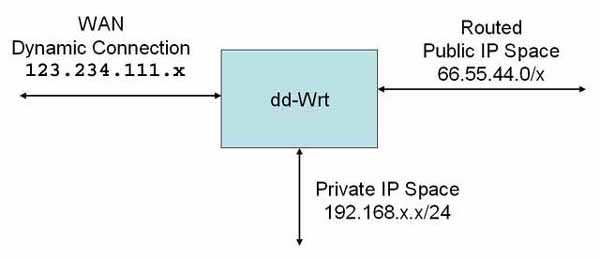
ISP public CIDR delivery
The network configuration has a either a static or dynamic IP address on
the
WAN side that is not in the same range as the routed subnet. This is a
common way provision static sub-nets in the US for AT&T and
Sonic.net
(probably others as well). Other providers may use similar methods of
delivering service using PPOE.
BASIC SETUP
Hard resetting the router to its initial state is recommended before
configuring using this procedure. 30/30/30 reset (read the WIKI).
Set up the connection for the WAN and LAN as you would if there were not a routed public CIDR block. The WAN connection should be set up per the ISP's directions for static, dynamic, or PPOE connection.
The LAN connection should likewise be set up as static or with DHCP to suit your network needs.
Stock dd-wrt is pre-configured so that the WAN is connected to vlan1 and the private network (LAN) and WIFI are connected to the internal bridge br0. In the case of WRT-54G-TM, this is port 5 for WAN and ports 1-4 for the LAN, respectively.
We will create a new vlan by splitting off two of the LAN ports for our routed public CIDR block.
WARNING: The port used for TFTP is port 1. This MUST remain on vlan0 so if you brick your router you can re-flash if after a hard reset.
To create vlan2, open the web interface to the router.
click SETUP click VLANs on line 0, unclick port's 3 and 4 on line 2, click port's 3 and 4 leave the bridge assigment on None click Apply Settings
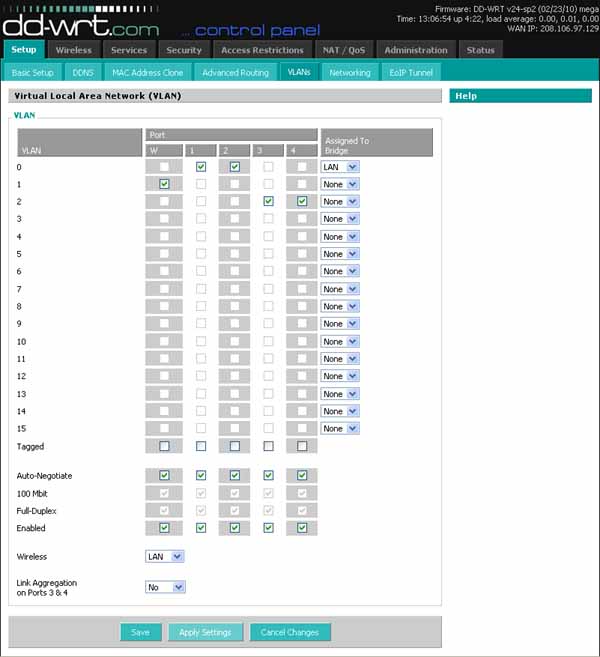
The next step is to set up the IP space for vlan2.
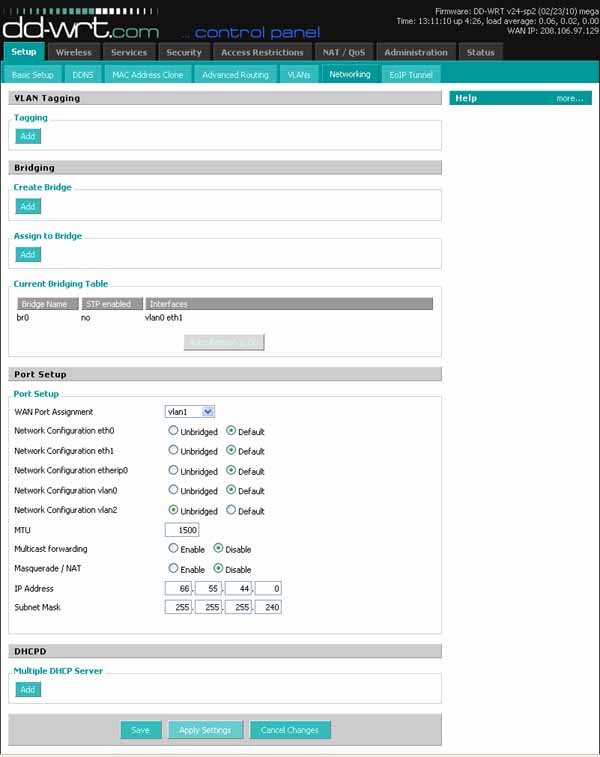
click Networking Port Setup menu, Network Configuration vlan2, click Unbridged Multicast Forwarding, click Disable Masquerade / NAT, click Disable
To finish the configuration we must add iptables rules for vlan2. First click Advanced Routing and verify that the router is in Gateway mode.
click Administration
click Commands
and enter this script in the command box
# gateway mode, vlan2 nat disabled
PUBCIDR="66.55.44.0/28"
MYIP="66.55.44.1"
# optional BASTION host
BASTION="66.55.44.2"
LANET="192.168.0.0/24"
WANIP=`ifconfig vlan1 | awk '/dr:/{gsub(/.*:/,"",$2);print$2}'`
# drop obvious spoof attempts
iptables -t nat -N chkspoof
iptables -t nat -A chkspoof -s 192.168.0.0/16 -j DROP
iptables -t nat -A chkspoof -s 172.16.0.0/12 -j DROP
iptables -t nat -A chkspoof -s 10.0.0.0/8 -j DROP
iptables -t nat -I PREROUTING -i vlan1 -j chkspoof
iptables -t nat -I PREROUTING -i vlan2 -j chkspoof
# disable NAT for PUBCIDR => WAN
iptables -t nat -I POSTROUTING -s $PUBCIDR -j ACCEPT
# NAT private lan to PUBLIC net
iptables -t nat -I POSTROUTING -o vlan2 -s $LANET -j SNAT --to-source $MYIP
# allow access to routed PUBLIC net
# block access to GUI from internet, allow from bastion host
iptables -I FORWARD -d $PUBCIDR -j ACCEPT
iptables -I FORWARD -d $MYIP -j DROP
iptables -I FORWARD -s $BASTION -d $MYIP -j ACCEPT
# block PUBCIDR -> LAN, allow LAN -> PUBCIDR
iptables -I FORWARD -i vlan2 -o br0 -j DROP
iptables -I FORWARD -m state --state ESTABLISHED,RELATED -j ACCEPT
# block access to GUI from PUBLIC net, allow from bastion host
iptables -I INPUT -s $PUBCIDR -d $MYIP -j DROP
iptables -I INPUT -s $BASTION -d $MYIP -j ACCEPT
# block access to WAN IP from PUBLIC net
iptables -I INPUT -s $PUBCIDR -d $WANIP -j DROP
click Save Firewall
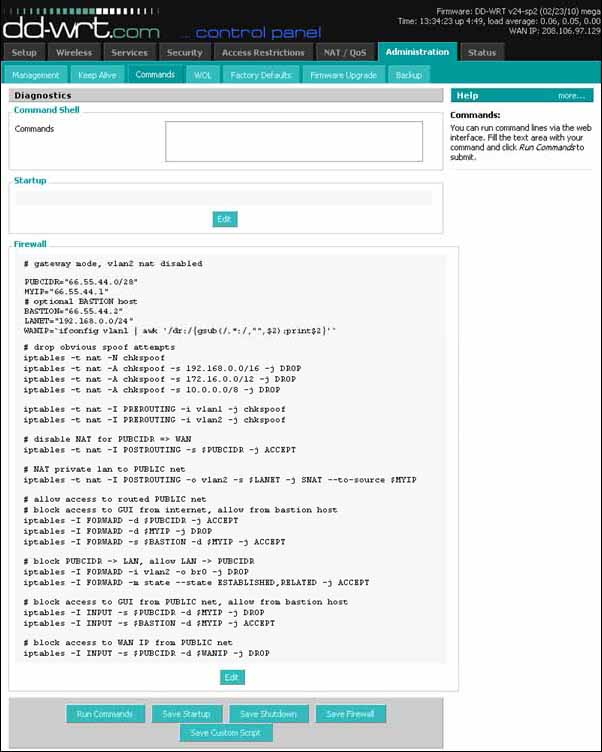
Done! reboot the router.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The original idea for this came from a procedure written by Odel Arbel
at:
setting-up-dmz-with-multiple-static-ips-on-an-office-lan-using-dd-wrt.The procedure I developed worked on 2.4 kernels but was awkward to say the least. When the requirement for a larger hash table size came up I posted to the dd-wrt forum in this thread:
ddwrt locks up with high active connection countand with the help of "phuzi0n, DD-WRT Guru" the procedure in this HOWTO was generated.
enjoy, Michael Robinton, michael(at)bizsystems.com